Skin Diseases Treatment are a broad range of conditions that affect the skin’s appearance, function, and overall health. These can range from temporary issues like rashes or infections to chronic conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne. Often triggered by genetics, environmental factors, or immune responses, skin diseases can significantly impact quality of life. Effective skin depends on accurate diagnosis and a tailored approach, addressing both the symptoms and underlying causes. From topical medications to advanced dermatological procedures, modern treatments offer relief and long-term skin health.
What are the Most Common Types of Skin Diseases?
Skin diseases can vary in cause, severity, and symptoms, but some types are more commonly observed across different age groups and skin types. Understanding these conditions is essential for early recognition, accurate diagnosis, and effective diseases treatment.
- Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Eczema is a chronic inflammatory condition that causes dry, itchy, and irritated skin, often seen in children but also affecting adults. It can be triggered by allergens, environmental stressors, or even stress, and while there is no cure, skin diseases treatment at home includes moisturizing regularly, avoiding known irritants, and using mild topical corticosteroids when needed.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder characterized by red, scaly patches of skin, commonly found on the scalp, elbows, and knees. This condition causes the skin cells to multiply too quickly, and treatment involves topical treatments, phototherapy, or systemic medications to manage flare-ups and reduce inflammation.
- Vitiligo: Vitiligo is a white skin disease marked by the skin pigmentation disorders in patches due to the destruction of melanocytes. While not contagious or life-threatening, it can significantly impact emotional well-being; white skin disease treatment may include topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, or depigmentation therapy depending on severity.
- Acne Vulgaris: Acne is one of the most common skin conditions, particularly among adolescents, caused by clogged pores, excess oil production, and bacterial growth. Treatment can range from over-the-counter cleansers and retinoids to prescription antibiotics or hormonal therapy in more severe cases.
- Fungal Infections (e.g., Ringworm, Athlete’s Foot): These infections are caused by dermatophytes and often affect moist areas of the body such as feet, groin, or underarms. Treatment typically includes antifungal creams or oral medications, and maintaining proper hygiene is key in both prevention and at home.
What Causes Skin Diseases Treatment?
Skin diseases can be triggered by a wide range of internal and external factors, including genetics, environmental exposure, infections, and immune responses. Understanding these causes is crucial for accurate diagnosis and determining the most effective skin diseases treatment for each condition.
- Genetic and Hereditary Factors: Many chronic skin conditions, such as psoriasis, eczema, and vitiligo, have a genetic component. Individuals with a family history of these disorders are at a higher risk, and white skin disease treatment for vitiligo, for example, often involves managing symptoms rather than curing the condition due to its genetic basis.
- Bacterial, Viral, and Fungal Infections: Pathogens like Staphylococcus bacteria, herpes simplex virus, and fungi such as Candida can lead to all types of skin diseases. These infections can cause conditions ranging from impetigo and warts to ringworm and yeast infections; treatments vary depending on the type of organism involved, and mild cases may respond to skin diseases treatment at home using medicated creams.
- Allergic Reactions and Irritants: Exposure to allergens (e.g., certain foods, pollen, or cosmetics) or irritants like harsh soaps and detergents can trigger contact dermatitis or hives. Identifying and eliminating the trigger is key, and treatment includes antihistamines or topical corticosteroids for symptom relief.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Some skin conditions arise when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, as seen in lupus or autoimmune-related eczema. These cases require medical intervention, as home treatments alone are typically insufficient to control inflammation and prevent skin damage.
- Hormonal Imbalances and Stress: Hormonal shifts during puberty, pregnancy, or menopause can lead to acne or flare-ups of existing skin conditions. Additionally, stress is known to worsen symptoms in diseases like psoriasis and eczema, highlighting the need for both medical and lifestyle-based approaches in skin diseases.
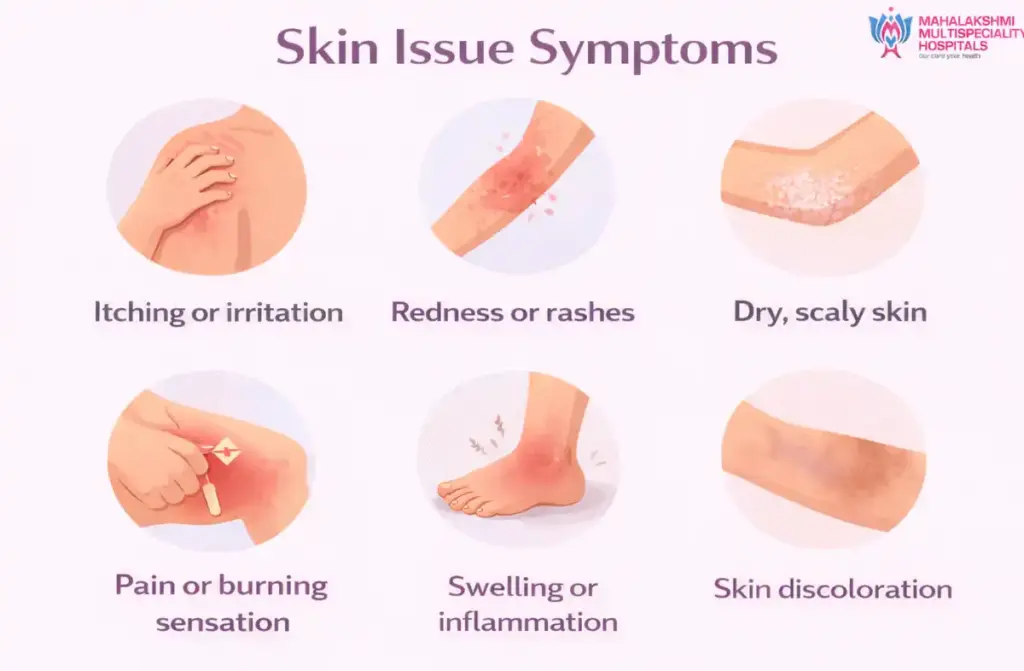
What are the Symptoms of Skin Diseases?
Skin disease symptoms can vary widely depending on the specific condition, its severity, and underlying causes. Recognizing these symptoms early helps guide timely and effective skin diseases treatment, whether medical or managed through skin diseases treatment at home.
- Redness and Inflammation: Persistent redness, swelling, or irritation is a common symptom in many inflammatory skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and contact dermatitis. These symptoms are often accompanied by warmth or tenderness and may respond to topical anti-inflammatory creams or gentle moisturizers.
- Itching or Burning Sensations: Intense itching or a burning feeling is frequently seen in allergic reactions, fungal infections, or dry skin conditions. If left untreated, constant scratching can break the skin and lead to secondary infections, making it important to apply suitable to soothe the area.
- Discoloration or Pigment Loss: Uneven skin tone, white patches, or dark spots may signal conditions like vitiligo, melasma, or fungal infections. White skin disease treatment for pigment loss often involves topical corticosteroids, light therapy, or immunomodulators, depending on the diagnosis.
- Scaly, Flaky, or Peeling Skin: Excessive dryness that causes the skin to peel or flake is common in all types of skin diseases including seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis. At-home treatment options often involve using emollients, gentle exfoliation, and medicated shampoos to reduce scaling.
- Rashes, Blisters, or Bumps: The appearance of sudden rashes, pus-filled blisters, or painful bumps can indicate bacterial, viral, or allergic skin conditions. Accurate identification is essential, as some cases require antibiotics while others can be managed with skin diseases at home using soothing agents or antiseptics.
How is a Skin Disease Diagnosed?
Skin disease diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, medical history, and sometimes lab tests to determine the correct treatment approach. Accurate identification ensures effective based on the specific condition.
- Visual Examination: A doctor assesses the skin’s appearance looking at color, texture, and lesion patterns to distinguish between all types of skin diseases.
- Medical and Family History: Personal and genetic background helps identify chronic or inherited conditions, guiding treatment, including white skin disease treatment.
- Skin Biopsy: A small sample may be taken for lab analysis when the diagnosis is uncertain or to confirm serious conditions.
- Allergy Testing: Patch tests detect allergic reactions, helping to eliminate triggers as part of skin diseases or medically.
- Lab Cultures: Swabs or scrapings identify bacterial, fungal, or viral infections to ensure accurate and targeted skin diseases treatment.
How are Skin Diseases Treated?
Skin diseases are treated based on their type and severity, ranging from home care to medical therapies. Proper treatment ensures symptom relief and prevents complications.
- Topical Medications: Creams with steroids, antifungals, or antibiotics help treat inflammation, infection, or irritation in all types of skin diseases.
- Oral and Injectable Drugs: Severe conditions may need pills or injections like antihistamines or biologics to manage widespread symptoms.
- Phototherapy: Controlled UV light is used in white skin disease treatment and conditions like psoriasis to improve skin appearance.
- Skin Diseases Treatment at Home: Mild cases can be managed with moisturizers, gentle cleansers, and avoiding irritants.
- Lifestyle Changes: A balanced diet, stress control, and proper hydration support long-term skin health and improve skin diseases treatment results.
How can I Prevent Skin Diseases?
Preventing skin diseases involves maintaining proper hygiene, protecting the skin from harmful exposures, and supporting overall immune health. These preventive measures reduce the risk of flare-ups, infections, and long-term complications, especially in individuals prone to all types of skin diseases.
- Practice Daily Skin Hygiene: Gently cleansing the skin with mild, fragrance-free products removes sweat, oil, and bacteria without disrupting the skin barrier. This is especially important for preventing fungal and bacterial infections, which often require skin diseases if left unmanaged.
- Avoid Triggers and Allergens: Identify and avoid personal irritants such as harsh soaps, detergents, or certain fabrics that can cause allergic reactions or dermatology treatment. Prevention is more effective than treatment, especially when dealing with chronic conditions requiring long-term at home.
- Protect Skin from Sun Exposure: Overexposure to ultraviolet rays can worsen existing conditions and trigger pigmentation issues. For example, white skin disease treatment often involves sun protection to prevent further depigmentation in vitiligo-affected areas.
- Keep Skin Moisturized: Dry skin is more prone to cracking, itching, and infection. Regular use of moisturizers helps maintain the skin’s barrier function, especially in eczema or psoriasis-prone individuals.
- Support Immune and Skin Health: A diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins A, C, and E, and proper hydration strengthens the skin’s natural defenses. A healthy immune system reduces susceptibility to infections and flare-ups in all types of skin diseases.
Conclusion
Skin Diseases Treatment affect people in various ways, but most can be effectively managed with the right care. Early diagnosis, tailored treatment, and consistent skin care routines are key to reducing symptoms and preventing flare-ups. From common conditions like acne and eczema to more complex issues such as vitiligo, a combination of medical and home-based treatments can lead to visible improvements. Maintaining proper hygiene, avoiding known triggers, and protecting the skin from sun exposure further support long-term results. With a proactive approach, individuals can manage their condition, improve skin health, and enhance overall well-being through effective and ongoing treatment.
Read also: H3N2 Influenza Virus Symptoms






